Power and Current Injection File Formats
The following sections discuss the types of input accepted, as well as the data input formats for the frequency-dependent network equivalent (FDNE) model.
There are multiple different types of input data accepted.
This is simply data from the Interface to Harmonic Impedance Solution component output file (ex. Harm.out). Please note however, that the Interface to Harmonic Impedance Solution component must be configured as follows in order to provide the data in the format needed:
The Impedance Output Type parameter should be selected as Phase Impedances.
The Frequency Output Units parameter should be selected as Hz.
The input data file contains the impedance of a multi-port network as a function of frequency.
If the scattering parameters data of the network is available, this option can be used. The reference impedances must be provided in the input data file.
The input data file contains the admittance of a multi-port network as a function of frequency.
The input data file contains the admittance of a multi-port network expressed in state space form. The state space realization of the admittance can be written as:
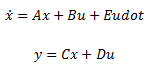
For N port system, A is a complex NS x NS matrix, B is a real NS x NC matrix, C is a complex NC x NS matrix, D is a real NC x NC matrix and E is a real NC x NC matrix.
The input data file contains the scattering parameters of a multi-port network expressed in state space form.
The input data file contains the sequence parameters of a multi-port network as a function of frequency.
Example formats are given below for each input data type.
The input file format coming from the Interface to Harmonic Impedance Solution is already formatted as required, provided that the parameter settings are set as described above. For more details on this input file format, see HIS Output File Format.
An input data file containing the impedance of a multi-port network, as a function of frequency must conform to the following format:
! Optional comment lines (must begin with '!') ! Enter the total ports (ex. NP=2), then the total frequency samples ! (ex. NF=501) 2 501 ! For each frequency sample, enter the impedance matrix in rectangular ! format Real(Z) Imag(Z). ! ! Example: ! ! f(1) ! Real(Z(1,1)) Imag(Z(1,1)) ! Real(Z(1,2)) Imag(Z(1,2)) ! Real(Z(1,3)) Imag(Z(1,3)) ! Real(Z(2,1)) Imag(Z(2,1)) ! Real(Z(2,2)) Imag(Z(2,2)) ! Real(Z(2,3)) Imag(Z(2,3)) ! ... ! Real(Z(NP,NP)) Imag(Z(NP,NP)) ! f(2) ! ... 10.0000000000000 0.174850482412908E+01 -0.795734349663449E+04 -0.207109997339879E-02 0.628728922650845E+00 -0.207109997339877E-02 0.628728922650845E+00 0.100096933317287E-01 0.132051171216790E+01 10.1859138805412 ... |
The input data file contains the admittance of a multi-port network as a function of frequency. This is the same format as Impedance Parameters above; simply swap Y matrix values for Z matrix values.
An input data file containing the scattering parameter data of a multi-port network must conform to the following format:
! Optional comment lines (must begin with '!') ! Enter the total ports (ex. NP=2), then the total frequency samples ! (ex. NF=501) 2 501 ! A reference resistance must be provided for each port. In this example, ! The number of ports is NP=2, therefore two resistances are provided: ! ! Example: ! ! R(1) ! R(2) ! ... ! R(NP) ! 100.0 100.0 ! Example: ! ! f(1) ! Real(S(1,1)) Imag(S(1,1)) ! Real(S(1,2)) Imag(S(1,2)) ! Real(S(1,3)) Imag(S(1,3)) ! Real(S(2,3)) Imag(S(2,3)) ! ... ! Real(S(NP,NP)) Imag(S(NP,NP)) ! f(2) ! ... 10.0000000000000 0.999678657861817E+00 -0.251299069941465E-01 -0.157942496334932E-03 0.358519576184203E-05 -0.157942496334932E-03 0.358519576184196E-05 -0.999451209037746E+00 0.264013378058848E-01 10.1859138805412 ... |
An input data file containing the admittance data as ABCD parameters must conform to the following format:
! Optional comment lines (must begin with '!') ! Enter the total ports (ex. NP=2), then the total number of states (i.e. ! the dimension of the A matrix (ex. NS=68). 2 68 ! Enter the real and imaginary parts of the A matrix, then the B matrix, then ! the C, D and E matrices. ! ! Example: ! ! A MATRIX (COMPLEX) ! ! Real(A(1,1)) Imag(A(1,1)) ! ... ! Real(A(NS,NS)) Imag(A(NS,NS)) ! ! B MATRIX (REAL) ! ! Real(B(1,1)) ! ... ! Real(B(NS,NS)) ! ! C MATRIX (COMPLEX) ! ! Real(C(1,1)) Imag(C(1,1)) ! ... ! Real(C(NS,NS)) Imag(C(NS,NS)) ! ! D MATRIX (REAL) ! ! Real(D(1,1)) ! ... ! Real(D(NS,NS)) ! ! E MATRIX (REAL) ! ! Real(E(1,1)) ! ... ! Real(E(NS,NS)) ! ! A MATRIX -0.476190498813596E+00 0.000000000000000E+00 -0.344849891474060E+04 0.000000000000000E+00 ... ! B MATRIX 0.100000000000000E+01 0.000000000000000E+00 ... ! C MATRIX -0.281633348985801E-14 0.000000000000000E+00 0.264927919633754E-11 0.000000000000000E+00 ... ! D MATRIX 0.833333333333331E-01 -0.144142218102473E-15 ... ! E MATRIX 0.000000000000000E+00 0.000000000000000E+00 ... |
An input data file containing the scattering data as ABCD parameters must conform to the following format:
! Optional comment lines (must begin with '!') ! Enter the total ports (ex. NP=2), then the total number of states (i.e. ! the dimension of the A matrix (ex. NS=68). 2 68 ! A reference resistance must be provided for each port. In this example, ! The number of ports is NP=2, therefore two resistances are provided: ! ! Example: ! ! R(1) ! R(2) ! ... ! R(NP) ! 100.0 100.0 ! Enter the real and imaginary parts of the A matrix, then the B matrix, then ! the C, D and E matrices. ! ! Example: ! ! A MATRIX (COMPLEX) ! ! Real(A(1,1)) Imag(A(1,1)) ! ... ! Real(A(NS,NS)) Imag(A(NS,NS)) ! ! B MATRIX (REAL) ! ! Real(B(1,1)) ! ... ! Real(B(NS,NS)) ! ! C MATRIX (COMPLEX) ! ! Real(C(1,1)) Imag(C(1,1)) ! ... ! Real(C(NS,NS)) Imag(C(NS,NS)) ! ! D MATRIX (REAL) ! ! Real(D(1,1)) ! ... ! Real(D(NS,NS)) ! ! E MATRIX (REAL) ! ! Real(E(1,1)) ! ... ! Real(E(NS,NS)) ! ! A MATRIX -0.544700620883931E+04 0.000000000000000E+00 -0.642728354625963E+04 0.000000000000000E+00 ... ! B MATRIX 0.100000000000000E+01 0.000000000000000E+00 ... ! C MATRIX -0.191041812478370E-05 0.000000000000000E+00 0.136037692862328E-03 0.000000000000000E+00 ... ! D MATRIX -0.785714285714284E+00 -0.799843438618597E-15 ... ! E MATRIX 0.000000000000000E+00 0.000000000000000E+00 ... |
An input data file containing the sequence parameter data must conform to the following format:
! F1, real(Zpos1), imag(Zpos1), real(Zzero1), imag(Zzero1) ! F2, real(Zpos2), imag(Zpos2), real(Zzero2), imag(Zzero2) ! F3, real(Zpos3), imag(Zpos3), real(Zzero3), imag(Zzero3) ! F4, real(Zpos4), imag(Zpos4), real(Zzero4), imag(Zzero4) ! ... ! Where, ! ! Fi = Frequency [Hz] ! Real(Zposi), imag(Zposi) = Real and imaginary parts of positive sequence ! impedance at frequency Fi. ! Real(Zzeroi),imag(Zzeroi)= Real and imaginary parts of zero sequence ! impedance at frequency Fi. ! 1.00,0.677,0.178,1.134,1.465 4.00,0.581,0.3454,1.234,2.2345 7.00,0.596,0.5345,2.5562.6435 10.00,0.601,0.746,3.788,2.745 ... |
Powerflow maintenance can be accomplished by either power or current injections.
This file is used to define voltage, angle, active and reactive power at terminals of the FDNE. Harmonics can be added as well by defining terminal conditions at different frequencies.
! Comment line NC ! Number of ports (should match FDNE interface ports) NF ! Number of power injections at different frequencies 0.1 ! Ramp time F1 ! Frequency V1 Angle1 P1 Q1 ! V, angle P,Q for port 1 for frequency F1 V2 Angle2 P2 Q2 ! V, angle P,Q for port 2 for frequency F1 V3 Angle3 P3 Q3 ! V, angle P,Q for port 3 for frequency F1 F2 ! Frequency V4 Angle4 P4 Q4 ! V, angle P,Q for port 1 for frequency F2 V5 Angle5 P5 Q5 ! V, angle P,Q for port 2 for frequency F2 V6 Angle6 P6 Q6 ! V, angle P,Q for port 3 for frequency F2 ... |
Alternatively if the current injections at the terminals of the FDNE are available, this can be directly entered.
This file is used to define voltage, angle, active and reactive power at terminals of the FDNE. Harmonics can be added as well by defining terminal conditions at different frequencies.
! Comment line NC ! Number of ports (should match FDNE interface ports) NF ! Number of power injections at different frequencies 0.1 ! Ramp time F1 ! Frequency Mag1 Angle1 ! Magnitude and angle for port 1 for frequency F1 Mag2 Angle2 ! Magnitude and angle for port 2 for frequency F1 Mag3 Angle3 ! Magnitude and angle for port 3 for frequency F1 F2 ! Frequency Mag4 Angle4 ! Magnitude and angle for port 1 for frequency F2 Mag5 Angle5 ! Magnitude and angle for port 2 for frequency F2 Mag6 Angle6 ! Magnitude and angle for port 3 for frequency F2 ... |
The units used are as follows:
|
Description |
Unit |
Frequency |
|
Hz |
V |
Magnitude of voltage at each terminal (port). RMS, port to ground. |
kV |
Angle |
Angle of the voltage (with respect to sinusoidal waveform). |
Deg. |
P |
Per port. |
MW |
Q |
Per port. |
MVAr |
Ramp Time |
Ramp time of the current sources. |
Seconds |
Mag |
Magnitude of the current (RMS). |
kA |
Ang |
Angle of the current. |
Deg. |